How To Help: When Tween and Teen Emotions Are Running High
During the Covid-19 home bound period, many of us may notice our tweens and teens emotions at an all time high and moving around like roller coasters. You might notice tears, frustration, yelling, down moods, isolating, and so on. This is partly due to the state of change and uncertainty being experienced in our society because of the pandemic. However, you are also likely getting a magnified look at what was already there.

Photo by Tengyart on Unsplash
Spending more time at home with our youth has given us an opportunity to get the inside scoop on how they are doing emotionally and how they are coping with the ups and downs of life.
I’ve chosen to see this as a gift, a true opportunity to get a pulse on what otherwise may be kept away from us most of the time. What is the gift in seeing my 12-year freak out because I asked them to turn off their video game? Or having a full out meltdown during an English assignment?

Photo by jLas Wilson on Pixabay
Well I’m glad you ask, because it may not be that apparent in those moments and I’m definitely not saying it is easy in any way.
What I am seeing is an opportunity to better understand how our young people are doing at the moment and how we can help teach them valuable ways to cope with the tough stuff.
I want to share three areas that you can focus on, as parents and supportive adults, to help your tweens and teens when emotions are running high.

Photo by Nathan Dumlao on Unsplash
Normalize and Allow
I saw a post the other day in my IG feed that said something like “we are not all in the same boat, but we are in the same storm”. Everyone, including our kids is experiencing the pandemic in unique ways. There are some good moments and some tough moments and I don’t think we can say this statement enough-
Whatever you are feeling is ok!
Normalize and allow means:
- Showing empathy and compassion
- Letting your kids know it is normal to respond with all kinds of emotions about what is going on
- Saying things like “this does really sucks right now”, “I know you’re frustrated right now”, “I’m missing __________ also”
- All feelings are ok
- This is different than all actions are ok (e.g. It’s ok to be pissed off- it’s not ok to punch a hole in the wall)
Spending more time at home with our youth has perhaps allowed us an opportunity to get the inside scoop on how they are doing emotionally
Noticing And Naming Feelings
This might seem like a no brainer and you may think, “my teen knows if they are sad, glad, mad, etc”. This may well be true but one thing I’ve noticed is that there is a tendency to focus on a narrow range of emotions such as excited, happy, scared, angry, sad, disgusted.
It can be helpful to develop your kids emotional vocabulary. This can help young people better understand their experience and express themselves. Also, this can help us as adults tune in and show our support.
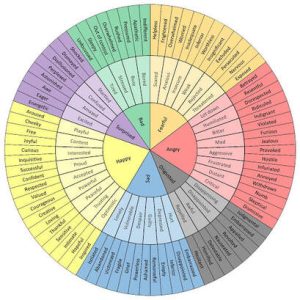
Emotion Wheel
In a moment of high emotions, it might be impossible to imagine introducing an extended emotional vocabulary, so that’s not the place to start with this one. You might start by printing out a feelings wheel and posting it somewhere, checking out on-line resources together or practicing using different words to express your own emotions. Research suggests the more vocabulary we have about our feelings, the more we develop ways to process them and the ability to figure out plans of action to cope.
Naming the emotion can simply start with “I’m feeling….”. Your tween or teen may not know what they are feeling all the time. In the beginning, we can encourage our kids to start saying “I’m feeling….”. This is the start of building awareness and noticing feelings.

Photo by Eye for Ebony on Unsplash
If your tween or teen is open to mindfulness in some way, and you may be surprised which ones are, you can try inviting them to try some short practices. Mindfulness is big with athletes right now with the perspective of sport being such a mindset game. Athletes are practicing mindfulness with their coaches and organizations. It has become so much more mainstream and so the invitation might be worth a try.
If your tween or teen is able to practice naming their feelings or at least acknowledge that they are experiencing a feeling you can invite them to check in with themselves.
Checking in means asking:
- Where do I feel this feeling in my body?
- How big or intense is it right now?
- What sensations do I notice- tight, tense, heavy, hot, light, pulsing, empty, numb, knotted, etc.
The more our kids can connect with a feeling and bring awareness to it, the more easily it will flow in and away. There are a couple of scripted practices that you can search for such as “labelling thinking and feeling” and “noticing your emotions”. Try this with many different feelings not just negatively experienced ones.
3 R’s of Emotional Literacy – Regulate, Relate and Reason
If you are familiar with Dr. Daniel Siegel’s hand brain model, it can be a really useful tool in understanding how our brain functions and how it responds to stress.
Dr. Siegel uses the expression of “flipping our lid” when our brain goes into fight or flight mode. When we are faced with something that is distressing or provokes big feelings, our brain detects a threat and jumps into a sympathetic state called fight or flight. What does this look like in our kids?
Well it could be yelling, shouting, tantrums, tears, meltdowns, shutdowns, self-harm, etc. Dr. Bruce Perry introduced the idea of 3R’s as 3 steps that parents can take to help support their children when they have “flipped their lids”.
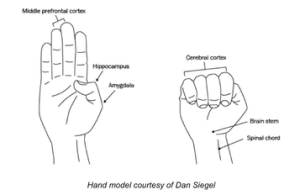
Hand Model courtesy of Dan Siegel
Regulation– This is the first step in settling and soothing the body and brain. This step gets “the lid” back on so that our kids can get their thinking brain back on-line. The more this skill is practiced, the more the brain builds new neural pathways that make regulation more automatic. You can coach your tweens and teens through these moments and you can also teach them to use these skills on their own.
Regulation means:
- Using our senses (tuning into what we can see, hear, feel, smell, taste)
- Movement- the best is patterned and repetitive movement such as walking, running, wall pushes, dancing, butterfly taps, drumming.
- Using sensory items like putty, pounding clay or pillows, weighted blankets, hugs
- Using calming smells like aromatherapy (test beforehand!!!), or a fresh smelling article of clothing or blanket
- Using sound like noise cancelling headphones or listening to music
- Focused breathing like slowing down our breath, finger or shape breathing, 4-7-8 breath

Photo by Marco Bianchetti on Unsplash
Relate– Now that “the lid” is back on, we are looking to care for their emotional centre. Connecting and reconnecting with our kids in that moment and letting them know we love them and are there for them and with them. Consider your own affect and your tone. It may be subtle, but if you offer a calm and loving presence vs. an agitated and cold presence, the outcome will likely be very different. Actively listening to our kids can help them feel connected and bring about more positively experienced emotions.
Reason– Once our kids are calmer, we are able to access the deeper and more reflective thinking. This might be where you come up with ideas on how to solve similar problems in the future. It might be where you talk about alternative behaviours and negotiate expectations and limits.
I saw in my IG feed that said something like “we are not all in the same boat, but we are in the same storm”.
So as emotions run high during this time, remember to normalize and allow, notice and name, and use the 3R’s to help our youth develop their best emotional coping skills.
If you found this post helpful, pass it on by emailing a friend or sharing it on Twitter or Facebook- Thanks!

Chantal Côté (she/her) is a psychologist and teen life coach living in Calgary, Alberta. After over a decade in non-profit and community mental health, Chantal started Pyramid Psychology, a practice dedicated to supporting teens – a population she is constantly amazed by. Chantal is on a mission to help 100,000 teen girls (and their parents) build bulletproof mindsets so they can weather the ups and downs of life. As part of this goal, Chantal has had the privilege of speaking at various events – virtual and live – to support teens and parents.
Outside of this passion, Chantal is often in nature, writing poetry, playing ball hockey and hanging out with her loved ones.
Each week, Chantal writes a blog article in response to issues she hears from the parents and teens she connects with.
If you have something you’d like to read more on – email ideas and questions to info@pyramidpsychology.com or DM us via Instagram or Facebook.







 Chantal Côté (she/her) is a psychologist and teen life coach living in Calgary, Alberta. After over a decade in non-profit and community mental health, Chantal started
Chantal Côté (she/her) is a psychologist and teen life coach living in Calgary, Alberta. After over a decade in non-profit and community mental health, Chantal started