How to Combat Anxiety – Part 4 of 4 Miniseries – Practical Ideas to Settle and Soothe- Visualization and Imagery
How can we use imagery and visualization to settle and soothe our minds and bodies from anxious, fearful, and negative thoughts?
Let’s continue the conversation on how to let our body and mind know, “thanks for keeping me on alert but I’m ok right now and I’ve got this”.
I wanted to be outdoors when recording, although I did sacrifice sound and video quality to some degree, I decided to go with it. Being outdoors is definitely my happy place and whenever I use guided imagery or visualization, some elements of nature always make their way in. Visualizing nature might also work for you or you might have some other things that really connect when it comes to using your imagination as a resource.
whenever I use guided imagery or visualization, some elements of nature always make their way in.

Photo by Canva
What is visualization and imagery?
Imagery or visualization involves using your imagination to help put your body and mind in a different state. In most cases, it is used to help create a more relaxed state but it can also help with things like focus and performance.
Imagining has the power to change brain activity

Photo by Canva
Our brains are pretty amazing. Connecting with our imagination and our thoughts is something that people are very interested in and that scientists have been increasingly researching especially in the fields of athleticism and mindfulness.
after an 8-week meditation program, the amygdala (brain’s smoke alarm) was less activated when exposed to emotional content

Photo by Canva
Research studying the brain of those who meditate or practice mindfulness on a regular basis have shown that brain activity changes during meditation. What’s even more interesting is that the changes that take place during meditation are maintained even when participants are not meditating. One study using FMRI (takes pictures of the brain and records brain activity) found that after an eight week meditation based program, the amygdala (our brain’s smoke alarm) was less activated when exposed to emotional content.
Why do we care to know this?!?!
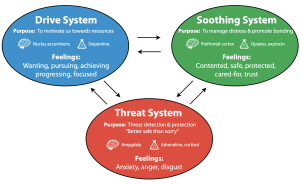
Well the amygdala is like the brain’s smoke alarm, it alongside with other brain structures, take the stimulus we receive in the world and helps our brain (and body) decide what to make of it- is this a threat? Is this enjoyable? Do I need to freak out right now? So if research on the brain is telling us that our amygdala activation is changing that is important to a society that has more recently been living in the crux of perpetual anxiety. It means we can play an active role in helping ourselves out when it comes to upsetting thoughts and feelings and our response.
The thing is that the emotions of fear and anxiety are based in the memory of something that was scary or in the anticipation that something terrible might happen which, “triggers a habitual fear response…… even if there is no actual present-moment threat”.

Photo by Canva
The take away- it is VERY good to have a brain and body that can respond to threat when we are in ACTUAL danger AND it is even better if we can help that brain and body to become super efficient at sifting through what is actually a threat and what is not.

Photo by Canva
Another way that imagery and visualization has been researched is in the realm of athletics. Imagining doing an activity, like a sport, prior to actually doing the activity can help our brain remember the neural pathways needed for that physical activity. Athletes can use imagery and visualization to improve physical performance and to perform under pressure- Amazing!
So that’s pretty cool and speaks to the power of visualization and imagery, but before I digress any further let me bring us back to using visualization and imagery to settle and soothe our minds and bodies when we are flooded with anxious, fearful, or negative thoughts and feelings.
What I like to use when it comes to settling and soothing the mind and the body are visualizations such as containment, safe place or safe state imagery. The reason I like these in particular is because I find they are very effective at kicking in the parasympathetic system (rest and relax) and I can access them any time.
Container Visualization
This visualization focuses on creating some imagery of a container or vessel of sorts that can hold upsetting, painful, or difficult thoughts and feelings until you are ready to come back to them. This is great for in the moment settling of the mind and body. The idea here is that you can use your imagination to put difficult thoughts and feelings “on the shelf” temporarily to be able to focus again or continue on with your day, but that you can come back to them when you feel supported to do so.
Here is an example of a guided visualization that is about 7 minutes long.
Safe Place Visualization
Safe place visualization can be a great tool to respond to overwhelming moments. Sometimes the idea of a safe place may be difficult for a person to imagine. In particular if your experiences hold trauma or spaces that generally felt unsafe. I will always invite clients to consider that the space may be one they’ve been before, one they imagine they want to go to one day, or perhaps it is a completely imagery place. At the end of a safe place visualization, you can also imagine a word or phrase that might help bring your mind and body back to this more relaxed and settled state at another time. An alternative is to take a few moments after the visualization to draw, paint, or write about the place. This can help it to stay with us in a meaningful way to come back to at another time, if that feels like an option.
it is very good to have a brain and body that can respond to threat when we are in ACTUAL danger AND it is even better if we can help that brain and body to become super efficient at sifting through what is actually a threat and what is not.
A note on making it more meaningful-
Introducing and using visualization and imagery to help settle your mind and body comes with a few considerations. In my experience, they can be very effective as a one off. If you are needing something in the moment and don’t plan on using it again, it is ok to access this practice once and you may see that it is quite helpful.
Saying that, I think the more you practice, the more benefit you will get from it. Just like in those studies looking at the effects of meditation and imagery for athletics on the brain, the more we activate certain parts of the brain, the more efficient our brain becomes at lighting those areas up.
There may be some scripts that work better for you than others. There are lots of videos, books, blogs, apps and websites that offer so many different types of visualization and imagery scripts. Some are specific to theme, timing, or for specific areas of life (sports performance, addictions, anxiety, stress, etc). I would really encourage you to look at some different options and see what fits for you. On that note, the voice and the pace of guided visualizations are unique. Have a listen to the first few seconds of some guided visualizations and if you don’t like the voice or something is just not sitting well for you, try something different!
Here are some resources to consider checking out:
https://psychcentral.com/lib/imagery-basic-relaxation-script/
https://www.innerhealthstudio.com/imagery-and-visualization.html
https://self-compassion.org/category/exercises/
https://www.developgoodhabits.com/best-mindfulness-apps/
https://www.mirecc.va.gov/cih-visn2/Documents/Patient_Education_Handouts/Visualization_Guided_Imagery_2013.pdf

Photo by Canva
If you found this post helpful, spread it by emailing to a friend or sharing it on Twitter or Facebook.
Happy imaginings!
 Chantal Côté (she/her) is a psychologist and teen life coach living in Calgary, Alberta. After over a decade in non-profit and community mental health, Chantal started Pyramid Psychology, a practice dedicated to supporting teens – a population she is constantly amazed by. Chantal is on a mission to help 100,000 teen girls (and their parents) build bulletproof mindsets so they can weather the ups and downs of life. As part of this goal, Chantal has had the privilege of speaking at various events – virtual and live – to support teens and parents.
Chantal Côté (she/her) is a psychologist and teen life coach living in Calgary, Alberta. After over a decade in non-profit and community mental health, Chantal started Pyramid Psychology, a practice dedicated to supporting teens – a population she is constantly amazed by. Chantal is on a mission to help 100,000 teen girls (and their parents) build bulletproof mindsets so they can weather the ups and downs of life. As part of this goal, Chantal has had the privilege of speaking at various events – virtual and live – to support teens and parents.
Outside of this passion, Chantal is often in nature, writing poetry, playing ball hockey and hanging out with her loved ones.
Each week, Chantal writes a blog article in response to issues she hears from the parents and teens she connects with. If you have something you’d like to read more on – email ideas and questions to info@pyramidpsychology.com or DM us via Instagram or Facebook.

























 Chantal Côté (she/her) is a psychologist and teen life coach living in Calgary, Alberta. After over a decade in non-profit and community mental health, Chantal started
Chantal Côté (she/her) is a psychologist and teen life coach living in Calgary, Alberta. After over a decade in non-profit and community mental health, Chantal started 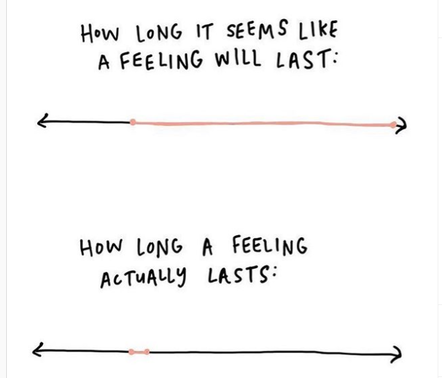













 Jessa is a counsellor that has recently completed her master of counselling degree through Athabasca University.
Jessa is a counsellor that has recently completed her master of counselling degree through Athabasca University.